Robotic process automation (RPA) is transforming how businesses operate — and the data proves it. From rapid adoption rates to cost savings and workforce impact, these stats reveal where RPA stands in 2025 and why it’s more than just a buzzword.
Let’s dive into the robotic process automation statistics driving automation forward.
What Is RPA and Why Does It Matter?
Robotic process automation is software that takes over repetitive tasks like entering data, processing invoices, or onboarding customers — things people usually do manually. Instead of wasting time on these routine jobs, RPA handles them quickly and accurately, reducing mistakes and speeding up workflows.
Businesses often spend a lot of time and money on these manual tasks that don’t add much value. With RPA, companies can reduce costs and avoid errors without hiring more people. It helps teams focus on work that actually needs human judgment, while bots handle the repetitive stuff. In short, RPA is a tool that makes operations smoother and helps businesses get more done with the same resources.
RPA Market Size and Key Trends
Companies are investing heavily in automation, shifting spending toward more cost-effective and higher-volume robot orders. Let’s look at the key stats shaping this evolving landscape.
1. The robotics market is expected to generate $50.8 billion in revenue in 2025. (Statista)
2. Service robotics is set to lead the market with an estimated revenue of $40.58 billion in 2025. (Statista)
3. Companies expect automated systems to account for 25% of their capital spending from 2023 to 2028. (McKinsey)
4. In Q3 of 2024, unit growth outpaced revenue growth at 14.1%, suggesting more cost-effective robots were ordered in higher volumes. (Association for Advancing Automation)
5. Within the automotive segment, orders for components surged by 61%, whereas orders from automotive OEMs declined by 15%. (Association for Advancing Automation)
6. From January to September 2024, North America recorded a total of 23,034 robot orders worth $1.45 billion — a 1.9% drop in units and a 2.2% decline in revenue compared to the same period in 2023. (Association for Advancing Automation)
7. In 2024, 31,311 robots were ordered across North America, generating $1.96 billion in revenue — representing slight annual increases of 0.5% in units and 0.1% in revenue. (Association for Advancing Automation)
8. Between July and September 2024, North American companies purchased 7,329 robots worth $475 million. (Association for Advancing Automation)
9. Robotics revenue is projected to grow at a 9.49% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2025 to 2029, reaching a market value of $73.01 billion by 2029. (Statista)
RPA Adoption by Industry
Different industries are ramping up their investments and adoption of robotics at varying rates, with retail, life sciences, and food sectors leading the way. Companies are also showing a clear preference for vendors offering full-service solutions that cover everything from hardware to support. Here’s a look at how these trends are playing out across sectors.
10. In the retail and consumer goods sectors, 23% of firms plan to invest over $500 million in robotics and automation. (McKinsey)
11. Among food and beverage companies, 15% report plans to spend more than $500 million on automation, while 8% of automotive firms say the same. (McKinsey)
12. Life sciences, pharmaceuticals, and biomedical sectors saw a 35% increase in robot orders, while the food and consumer goods sector grew by 13%. (Association for Advancing Automation)
13. Nearly two-thirds (62%) of companies say they prefer robotics vendors that provide a full-service model — including hardware, software, system integration, maintenance, and support. (McKinsey)
14. Year-over-year growth for specific non-automotive industries was significant, with food and consumer goods up 60%, life sciences/pharma/biomed up 43%, and metals up 8%. (Association for Advancing Automation)
15. Industrial robot installations in Europe increased by 9% in 2023, reaching a record 92,393 units. Of these, 80% (73,534 units) were installed within the European Union, marking a 2% rise from the previous year. (International Federation of Robotics)
16. 83% of senior leaders have either implemented or are planning to adopt automation in palletization and packaging, making it the most mature use case on the list. (McKinsey)
17. Almost 80% of RPA adoption is seen in goods receiving, unloading, and storage, highlighting backend logistics as another leading area for automation. (McKinsey)

18. Six years after their introduction in 2018, RPA and optical character recognition (OCR) technologies have finally become mainstream. Nearly 74% of respondents are already using RPA, and 50% are using OCR. (Deloitte)
19. Successful implementation of automation boosts process efficiency, with reported cost savings ranging from 25% to 75%. (ResearchGate)
RPA Adoption Challenges
Adopting RPA isn’t always straightforward — many companies face roadblocks that slow progress. From gaps in internal expertise to challenges finding the right vendors, these hurdles highlight why automation success depends on more than just technology.
20. About 42% of companies struggle to find end-to-end robotics solution providers that operate effectively across different regions. (McKinsey)
21. In the retail and consumer goods space, around 60% of respondents cite limited internal knowledge and uncertainty about ROI as key obstacles to adopting robotics. (McKinsey)
22. Twenty-two percent of organizations do not have a clear and accepted vision for intelligent automation. (Deloitte)
23. Forty-one percent of organizations lack an enterprise-wide intelligent automation strategy. (Deloitte)
RPA Market Growth by Region
RPA and industrial robotics adoption is expanding rapidly — but not evenly — across the globe. While markets like China and India are breaking records, others are showing steadier growth or focusing on density and efficiency. Here’s how different regions are shaping the global robotics landscape.
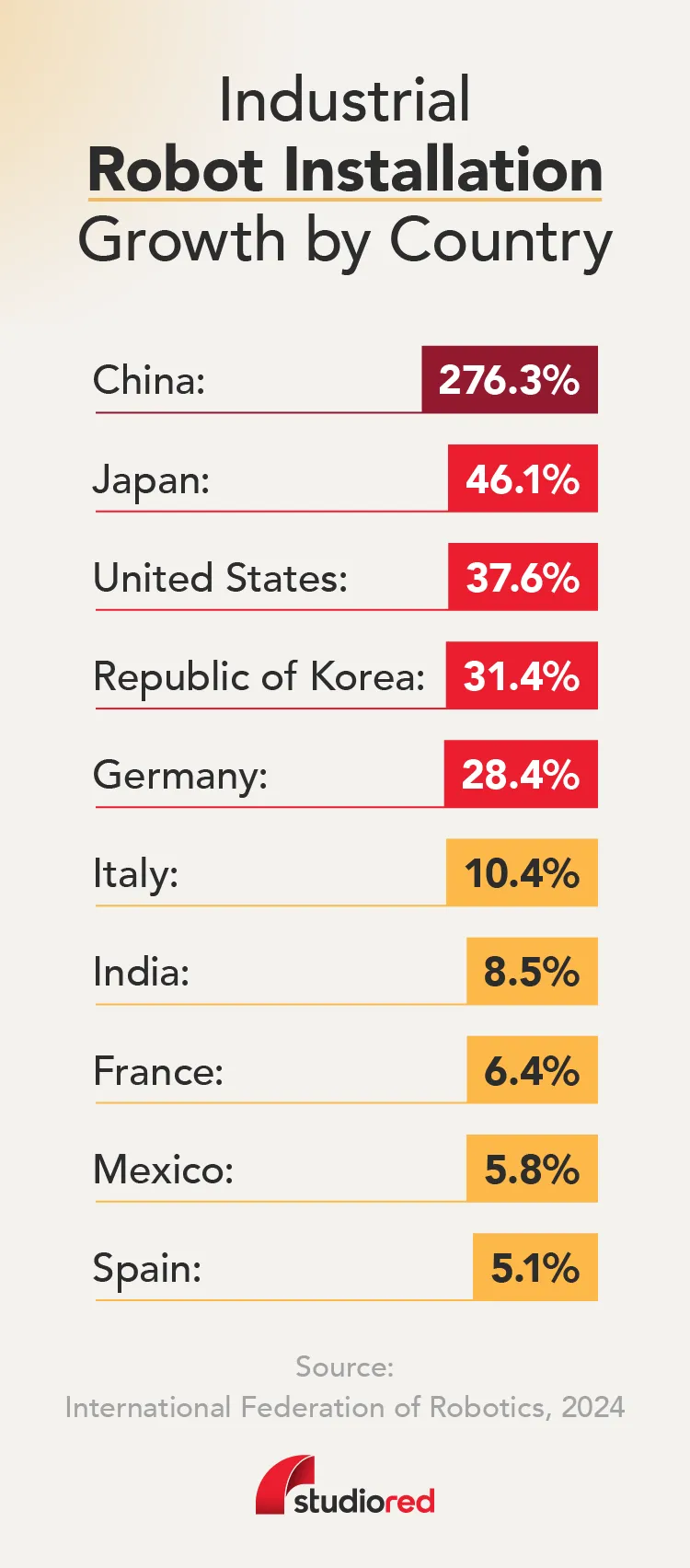
24. China is by far the world’s largest market, accounting for 51% of all industrial robot installations in 2023 — 276,288 units in total. (International Federation of Robotics)
25. Japan held its position as the second-largest market for industrial robots in 2023, with 46,106 units installed. (International Federation of Robotics)
26. The Republic of Korea’s industrial robot market remained steady in 2023, with 31,444 installations — down just 1% year-over-year. It ranked as the fourth-largest market globally, following China, Japan, and the United States. (International Federation of Robotics)
27. The European Union has a robot density of 219 units per 10,000 employees — up 5.2% from the previous year. Germany, Sweden, Denmark, and Slovenia all rank in the global top 10 for robot density. (International Federation of Robotics)
28. Robot sales in North America grew 8.8% in Q3 2024 compared to Q3 2023, with 7,329 units sold, totaling $475 million in revenue. (Association for Advancing Automation)
29. India, one of the fastest-growing Asian economies, saw robot installations surge by 59% in 2023, reaching a record high of 8,510 units. Demand from the automotive sector alone jumped 139% to 3,551 units, driven by strong contributions from both car manufacturers and their suppliers. (International Federation of Robotics)
How RPA Is Shaping the Future of User-Centered Digital Products
2025 saw the RPA market pick up again, and it’s projected to keep growing through 2026 and 2027. There’s no indication that the broader long-term upward trend in robotics will slow down anytime soon.
As automation becomes more integrated into everyday experiences, the way people interact with products is also changing.
“If you are looking at things like self-checkout machines, self-serve soda or coffee machines, and even cars, automation has allowed for a lot of technology to be hidden behind a screen — and that screen is the main point of interaction,” says –Diego Almaraz, StudioRed Industrial Designer.
This shift makes user interface design more critical than ever, as it’s often the only touchpoint between the user and increasingly complex systems running in the background.
If you’re building a product that blends smart automation with a seamless user experience, StudioRed can help you design and engineer it end-to- end. Contact us today!







